

- #WIRESHARK PORTABLE NO INTERFACES FOUND ANDROID#
- #WIRESHARK PORTABLE NO INTERFACES FOUND FREE#
- #WIRESHARK PORTABLE NO INTERFACES FOUND MAC#
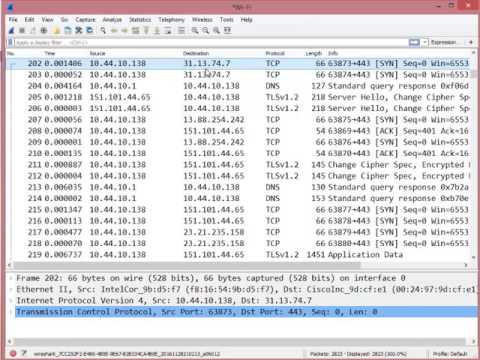
Length: This column shows you the length of the packet in bytes.Protocol: This is the type of packet, for example, TCP, DNS, DHCPv6, or ARP.Destination: This is the address of the destination of that packet.Source: This is the address of the system that sent the packet.You can change this value in the Settings menu if you need something different displayed. Time: This column shows you how long after you started the capture that this packet got captured.The bracket indicates that this packet is part of a conversation. No.: This is the number order of the packet that got captured.
#WIRESHARK PORTABLE NO INTERFACES FOUND ANDROID#
Here are some details about each column in the top pane: Application android file transfer for mac. You can also tell if the packet is part of a conversation. When you click on a packet, the other two panes change to show you the details about the selected packet. The Packet List, the top pane, is a list of all the packets in the capture. Wireshark shows you three different panes for inspecting packet data.
#WIRESHARK PORTABLE NO INTERFACES FOUND MAC#
Ettercap matches Wireshark’s portability because it can run on Windows, Linux, Unix, and Mac OS.
#WIRESHARK PORTABLE NO INTERFACES FOUND FREE#
As Wireshark is a well-known hacker tool, the Ettercap claim puts it in the same category and they are both free to use. Ettercap’s website makes no secret of the fact that it was designed to facilitate hacking. Related: Fix Common WireShark Startup ” no interfaces found” Issue. It is important to know if you can see the wireless interface in your Linux environment. Accessing the Wireless Interface in Linux on a Stand Alone System. Application > Kali Linux > Top 10 Security Tools > Wireshark. In Kali Linux you can start Wireshark by going to. But once Wireshark and your environment are set up properly, all you have to do is change tabs to view decrypted data. Step 1: Start Wireshark and capture traffic.
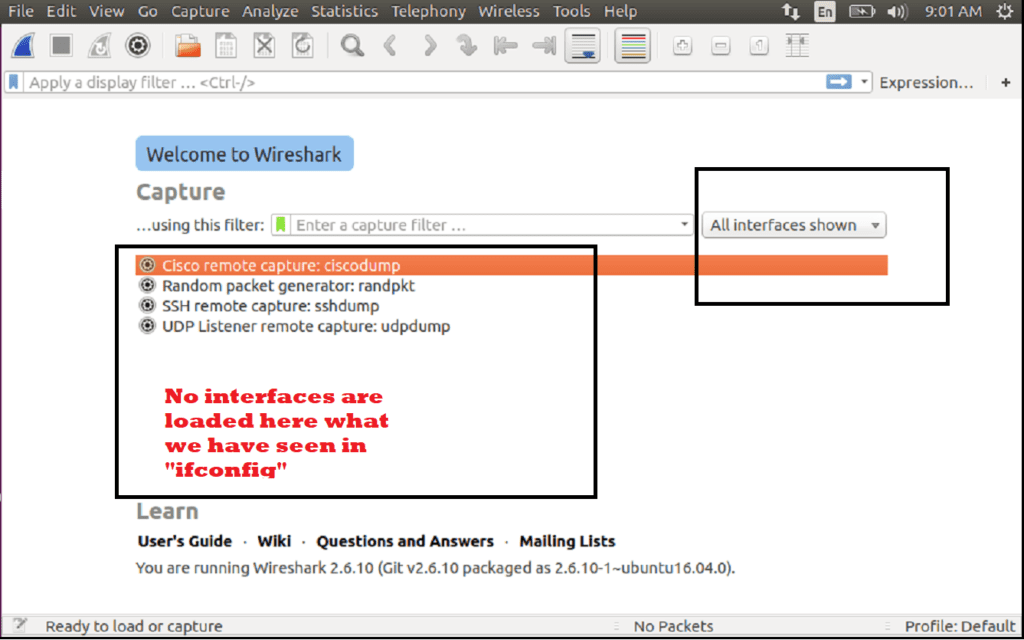
Cryptography is complicated, and the standards are constantly changing to be more secure. The Windows VM communicates normally with the outside network. Wireshark shows interfaces en0, en1, en3 and lo0, but ifconfig shows vmnet1 and vmnet8 I want to sniff traffic between the Mac host and a Windows VM (NAT), but the traffic never shows up in Wireshark. I'm trying to sniff traffic between my Leopard (10.5.7) host using Wireshark 1.0.2. Just like running tcpdump -D vs sudo tcpdump -D, the first one won't show any of the interfaces, won't compalain/prompt for sudo privileges either. You need to be superuser in order to be able to view interfaces. For.nix OSes, run wireshark with sudo privileges. If you are running Wireshark 1.4 or later on a.BSD, Linux, or macOS system, and it's built with libpcap 1.0 or later, for interfaces that support monitor mode, there will be a 'Monitor mode' checkbox in the Capture Options window in Wireshark, and a command line -I to dumpcap, TShark, and Wireshark.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
